Linux

Intel is once again investing in Linux development. The company has recently posted several job openings aimed at strengthening its Linux graphics driver and GPU software teams, signaling continued interest in improving Intel hardware support on the open-source platform.
For Linux users, especially gamers and developers, this could mean faster improvements to Intel’s graphics stack and stronger support for modern workloads.
New Roles Focused on Linux Graphics
Intel has listed multiple GPU Software Development Engineer positions, many of which specifically focus on Linux graphics technologies. These roles involve working on the full graphics stack, including firmware, kernel drivers, and user-space components used by applications and games.
The responsibilities for these positions include:
-
Developing and optimizing Intel GPU drivers for Linux
-
Improving the Linux graphics stack, including kernel DRM drivers and Mesa components
-
Working with graphics APIs and tools used by modern applications
-
Ensuring compatibility across desktop, workstation, and data-center hardware
The job listings also emphasize experience with C/C++ development and the Linux kernel graphics ecosystem, highlighting the technical depth required for these roles.
Linux Gaming Is Part of the Plan
One of the more notable details from the job postings is the mention of Linux gaming technologies such as Wine and Proton. These compatibility layers allow Windows games to run on Linux, making them central to platforms like SteamOS and the Steam Deck.
Intel’s focus on these tools suggests the company wants its GPUs to perform well not just in enterprise workloads but also in gaming environments. That aligns with the growing popularity of Linux gaming driven by:
-
Valve’s Proton compatibility layer
-
Vulkan-based graphics APIs
-
The success of devices like the Steam Deck
Beyond Gaming: HPC and Data Center Work
While gaming support is part of the focus, the hiring effort isn’t limited to consumer graphics. Intel is also recruiting engineers for areas such as:
-
High-performance computing (HPC)
-
AI and machine-learning workloads
-
Middleware development for supercomputing systems
-
Cloud and data-center GPU optimization
These roles indicate Intel’s broader strategy to strengthen Linux across multiple sectors, from desktops and laptops to supercomputers and cloud infrastructure.

The developers behind AerynOS have released AerynOS 2026.02 Alpha, the latest development snapshot of the independent Linux distribution previously known as Serpent OS. This new release continues the project’s rapid evolution, bringing updated packages, improved build tools, and new installation options while the system remains in an early testing stage.
Although still labeled as an alpha-quality release, the new ISO gives enthusiasts and developers a chance to explore the direction AerynOS is taking as it builds a modern Linux platform from scratch.
A Modern Atomic Approach
AerynOS aims to rethink how Linux distributions handle updates and package management. The project focuses on atomic-style updates, meaning system changes are applied as a complete transaction rather than individual package installs. This approach helps reduce the risk of partially completed updates leaving a system in a broken state.
Unlike some atomic distributions, however, AerynOS does not rely on an immutable filesystem, allowing users to retain flexibility and customization while still benefiting from safer update behavior.
Updated Desktop Environments
The 2026.02 alpha release ships with several modern desktop environment options:
-
GNOME 49.4 as the default desktop
-
COSMIC 1.0.8, System76’s emerging desktop environment
-
KDE Plasma 6.6.1 available as an alternative session
These updates provide users with multiple modern desktop choices while ensuring compatibility with the latest frameworks and desktop technologies.
New Core Software and Components
AerynOS 2026.02 also brings a large batch of software updates across the system stack. Some of the notable versions included in the release are:
-
Linux kernel 6.18.15 LTS
-
Firefox 148
-
PipeWire 1.6
-
Wine 11.3
-
Waybar 0.15
-
Mesa/Nesa graphics drivers 26.x
Together, these updates ensure that the development snapshot reflects a modern Linux software ecosystem while improving compatibility with newer hardware.
Improved Development Tooling
A significant portion of the February development cycle focused on improving the distribution’s internal tooling:
-
Moss, the package manager, has been optimized for faster performance.
-
Boulder, the package build system, now automates more recipe creation and version handling.
The Armbian project has released Armbian 26.02, the latest update to the lightweight Linux distribution designed specifically for ARM and RISC-V single-board computers (SBCs). Known for its stability and hardware optimization, Armbian continues to evolve with improved hardware support, new desktop options, and updated core components in this release.
A Linux Distribution Tailored for SBCs
Armbian is built on top of Debian or Ubuntu, providing optimized system images for single-board computers such as Orange Pi, Banana Pi, and ODROID devices. The project focuses on stability, performance, and long-term maintenance for embedded and development boards.
With the 26.02 release, the developers continue that mission by refining support for modern hardware platforms and improving the overall software stack.
Powered by Linux 6.18 LTS
One of the biggest upgrades in Armbian 26.02 is the transition to Linux kernel 6.18 LTS, which brings improved driver support, performance enhancements, and better compatibility for newer SBC hardware.
The newer kernel helps ensure that Armbian remains compatible with evolving chipsets while maintaining stability across its supported devices.
New Board Support
This release expands Armbian’s hardware ecosystem with support for several new boards, including:
-
SpacemiT MusePi Pro
-
Radxa Rock 4D
-
Orange Pi RV2
-
ODROID M2
These additions reflect Armbian’s ongoing focus on supporting emerging ARM and RISC-V development boards used by hobbyists, developers, and embedded system builders.
Desktop Improvements
Armbian 26.02 also introduces expanded desktop options:
-
RISC-V XFCE desktop images for supported RISC-V systems
-
Restored KDE Neon desktop builds
-
Updated desktop targets based on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
These changes give users more flexibility when choosing between lightweight environments or more full-featured desktop setups.
Enhancements to Armbian Tools
The Armbian ecosystem itself has also received improvements. The Armbian Imager utility, used to flash OS images to SBC storage devices, now features:
-
Faster image decompression
-
Code signing for improved security on macOS and Windows
-
AI-assisted translation support
-
A new settings panel with additional developer options

Excitement in the open-source world is rising as the Linux kernel project moves toward the next major release: Linux kernel 7.0. While a major version number might sound like a dramatic overhaul, the reality is a lot more steady progress, and that’s part of what makes the Linux kernel so reliable and trusted. The first release candidate (RC1) for Linux 7.0 has already been published, and developers are entering the final stretch toward a stable release expected around mid-April 2026.
An Evolution, Not a Revolution
Linus Torvalds, the creator and lead maintainer of the Linux kernel, officially confirmed that the next version after Linux 6.19 will be dubbed Linux 7.0. In the announcement, he made clear that the jump to “7.0” isn’t tied to any monumental architectural upheaval, it’s a practical naming decision made partly to keep version numbers manageable.
That tradition continues a long-standing pattern: kernel series are often numbered until they reach higher minor versions (like 6.19), and then the major number increments, even if the changes are incremental and largely additive rather than breaking.
Inside the 7.0 Development Cycle
The Linux 7.0 cycle opened with the merge window, during which new code from contributors around the world is accepted. With the release candidate phase now underway, the focus has turned toward stabilization and testing.
The 7.0-rc1 announcement notes that this cycle saw a “smooth” merge window with relatively few major boot failures reported on the lead developer’s own test machines, a good sign for the kernel’s broad hardware support.
Expected Improvements
While the final changelog for the stable 7.0 kernel will only be known when it ships, several themes stand out from early previews and reporting:
1. Broad Hardware EnablementDriver updates make up a significant portion of the changes so far, helping Linux support the latest CPUs and SoCs from vendors like Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm. Early testing indicates enablement for new families such as Intel Nova Lake and AMD Zen 6, which will be important for next-generation laptops, desktops, and servers.
2. Performance and ResponsivenessKernel maintainers and community reports suggest that performance improvements are part of the 7.0 trend. Although specifics are still emerging, the kernel’s scheduler and memory management subsystems tend to see ongoing optimization as workloads diversify.
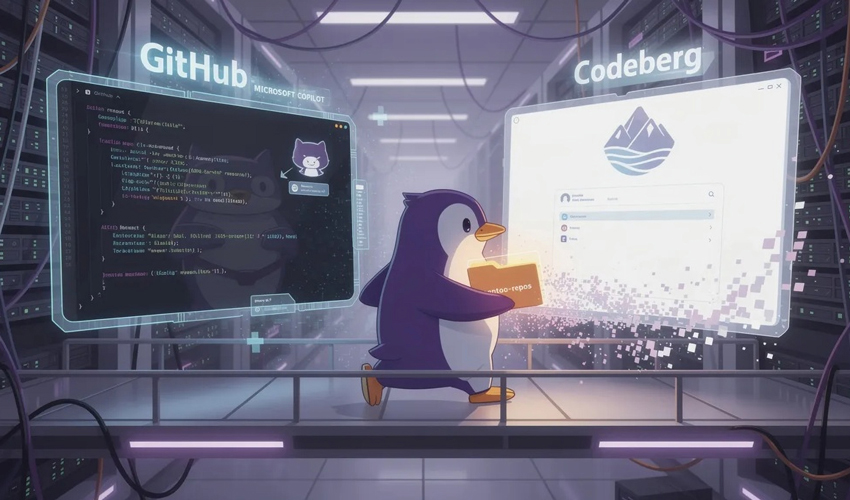

Introduction
The Gentoo Linux project has begun transitioning parts of its infrastructure away from GitHub and toward Codeberg, a Git hosting platform built on open-source principles. The move reflects growing concerns within parts of the open-source community about centralized hosting, proprietary AI integrations, and long-term platform independence.
While Gentoo has used GitHub for collaboration and code hosting in recent years, maintainers are now signaling a preference for a platform that aligns more closely with their philosophical roots.
Why the Shift?
One of the underlying motivations behind the move involves concerns around Microsoft’s expanding integration of AI tools like Copilot into GitHub’s ecosystem. While Copilot is optional and not mandatory for users, its presence has sparked debate within open-source communities about:
-
Code usage for AI model training
-
Transparency around data handling
-
Vendor control over open-source workflows
-
The long-term independence of community projects
Gentoo, a distribution known for its strong emphasis on freedom, customization, and user control, appears to be taking a cautious approach by diversifying its infrastructure.
Why Codeberg?
Codeberg is a community-driven Git hosting service powered by Forgejo, a fully open-source Git platform. Unlike GitHub, Codeberg operates as a non-profit organization and positions itself as an ethical alternative focused on transparency and sustainability.
Key characteristics include:
-
Open-source infrastructure
-
No proprietary AI tooling baked into the platform
-
Community governance model
-
Emphasis on privacy and minimal tracking
For a project like Gentoo, deeply rooted in open-source philosophy, these factors carry weight.
What This Means for Gentoo Users
For end users, the transition may not immediately change how Gentoo is installed or maintained. However, it could affect:
-
Where source code repositories are officially hosted
-
Where developers submit patches and pull requests
-
Contribution workflows for maintainers
Over time, the move could also reduce dependency on large corporate platforms, ensuring Gentoo retains autonomy over its infrastructure.
A Broader Trend in Open Source
Gentoo is not alone in reassessing its hosting platforms. Across the open-source world, projects have increasingly explored alternatives such as:
-
Codeberg
-
SourceHut
-
Self-hosted Git solutions

The open-source wearable ecosystem just received a major upgrade. AsteroidOS 2.0 has officially been released, bringing new life to Linux-based smartwatches and giving aging hardware a fresh purpose. Built by a passionate community of developers, AsteroidOS continues to push the idea that wearable technology can remain open, customizable, and free from vendor lock-in.
For users who prefer control over their devices, and for those with older smartwatches gathering dust, AsteroidOS 2.0 represents a compelling alternative to proprietary smartwatch platforms.
What Is AsteroidOS?
AsteroidOS is an open-source operating system designed specifically for smartwatches. Originally developed as a replacement for discontinued or unsupported Android Wear devices, the project has grown into a full Linux-based wearable platform.
Unlike closed smartwatch systems, AsteroidOS emphasizes:
-
Privacy-first design
-
Minimal background tracking
-
Full user control
-
Community-driven development
It runs on supported legacy devices and allows users to repurpose smartwatches that manufacturers have long abandoned.
What’s New in AsteroidOS 2.0
Version 2.0 is one of the most significant updates in the project’s history. While the philosophy remains the same, this release introduces meaningful improvements across usability, performance, and compatibility.
Modernized InterfaceAsteroidOS 2.0 brings a refreshed UI that feels smoother and more intuitive. Navigation between apps and watch faces is more fluid, and animations have been optimized for improved responsiveness on older hardware.
Improved Power ManagementBattery life is critical on wearables. The new release refines power-saving behaviors and background process handling, helping extend usage time between charges, especially important for devices with aging batteries.
Enhanced Bluetooth ConnectivityConnectivity improvements allow more reliable pairing with companion apps, notifications, and syncing features. Stability and compatibility with modern smartphones have been strengthened.
Updated Core StackUnder the hood, AsteroidOS 2.0 ships with updated components from the Linux ecosystem, ensuring better hardware compatibility and security fixes.

The Document Foundation has officially released LibreOffice 26.2, the latest major update to the widely used open-source office suite. With improvements spanning performance, user interface refinements, document compatibility, and accessibility, this version continues LibreOffice’s mission to provide a powerful, community-driven alternative to proprietary office software.
LibreOffice 26.2 is available for Linux, Windows, and macOS, offering consistent functionality across platforms while keeping full control in the hands of users.
What’s New in LibreOffice 26.2
While LibreOffice updates often focus on incremental refinement rather than radical redesign, version 26.2 introduces several meaningful enhancements that improve daily workflows.
Improved Performance and StabilityPerformance remains a priority. LibreOffice 26.2 includes:
-
Faster document loading, especially for large spreadsheets and presentations
-
Reduced memory usage in complex Calc files
-
Improved stability when handling heavily formatted documents
These optimizations make the suite feel more responsive across both modern systems and older hardware.
Enhanced Microsoft Office CompatibilityCompatibility continues to improve with each release. LibreOffice 26.2 delivers:
-
More accurate rendering of DOCX, XLSX, and PPTX files
-
Better support for advanced formatting and tracked changes
-
Improved handling of embedded objects and charts
For users collaborating with Microsoft Office users, these refinements reduce formatting surprises and make document exchange smoother.
Refined User InterfaceLibreOffice 26.2 builds upon its modern UI framework with:
-
Polished icon themes and improved scaling on high-resolution displays
-
Better dark mode integration across platforms
-
Smoother transitions in NotebookBar layouts
-
Improved accessibility for keyboard navigation and screen readers
The result is a cleaner, more cohesive experience without disrupting long-time users.
Writer ImprovementsLibreOffice Writer gains several practical enhancements:
-
More reliable footnote and endnote management
-
Improved table formatting controls
-
Expanded language and grammar tool integration
These updates benefit users creating academic papers, reports, and long-form documents.
Calc EnhancementsSpreadsheet users will notice:

In a development that has energized the Linux gaming community, GOG (Good Old Games) has officially confirmed that it is working on native Linux support. While GOG has long provided Linux installers for select titles, this announcement signals something more substantial: deeper platform integration and a renewed commitment to Linux as a first-class gaming environment.
For Linux users who value DRM-free software and ownership rights, this could be a significant turning point.
Why This Matters
GOG has built its reputation on offering DRM-free games that users truly own, free from online activation requirements and restrictive launchers. However, Linux users have historically faced a mixed experience:
-
Some games included native Linux builds
-
Others required manual setup through Wine or Proton
-
The GOG Galaxy client itself lacked native Linux support
While community tools like Heroic Games Launcher and Lutris filled the gap, the absence of official Linux support for the Galaxy ecosystem left many users dependent on workarounds.
Now, with GOG confirming active development of native Linux support, that gap may finally begin to close.
What Native Support Could Include
Although full details have yet to be finalized, “native support” could realistically mean several improvements:
-
An official GOG Galaxy client for Linux
-
Better integration with Proton or Wine when needed
-
Unified cloud saves and achievements on Linux
-
Streamlined game installation and updates
-
Official support channels for Linux users
If implemented properly, this would allow Linux gamers to enjoy the same ecosystem experience as Windows users without third-party bridges.
The Timing Makes Sense
The announcement comes at a moment when Linux gaming is stronger than ever:
-
The Steam Deck has normalized Linux as a gaming platform
-
Proton compatibility has reached impressive levels
-
Vulkan drivers and Mesa development continue advancing
-
Distros like Bazzite and Nobara are built specifically for gaming
With more gamers exploring Linux in 2026, GOG’s move may be both strategic and overdue.
What It Means for the Linux Gaming Ecosystem
If GOG delivers robust native support, several ripple effects could follow:
-
Increased confidence from developers to release Linux builds
-
More competition in the Linux game storefront space
-
Improved DRM-free game adoption among Linux users